BtaEX0031492 @ bosTau6
Exon Skipping
Gene
ENSBTAG00000014269 | SCARB1
Description
Bos taurus scavenger receptor class B, member 1 (SCARB1), mRNA. [Source:RefSeq mRNA;Acc:NM_174597]
Coordinates
chr17:53263825-53273723:+
Coord C1 exon
chr17:53263825-53263971
Coord A exon
chr17:53267786-53267914
Coord C2 exon
chr17:53272786-53273723
Length
129 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
TTAGCTTGGTTATCTTCTAGGAG
3' ss Score
6.64
5' ss Seq
TAGGTGGGT
5' ss Score
5.56
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
AGTGGAGCAATGGAGGGTGAGACCCTTGAGACGTTCTATATCCAGCTGGTGTTGATGCCCAAAGTGCTACACTATGCCCAGTATGTGCTCCTTGCCCTGGGCTGCGTCCTACTGCTCATCCCCATCATCTACCAAATCCGGAGCCAA
Seq A exon
GAGAAATGCTATTTATTTTGGATTAGTTTTAAAAAGGGCTCAAAGGATAAGGAGGCCGTTCAGGCCTATTCTGAATTCCTGATGACATCAGCTCCCAAGGGAACTGTACTGCAAGAAGCAAGACTGTAG
Seq C2 exon
GGTTCCAAAGATGCCATCAGCCAGCCCTGTCTGGCCACTCAGCCAGACCAACTTCCCAGCCCCTACACCCCGCTTCTTCAGGACTCGCTCCGTGGACAGCCCACCAGTCCCAAAGTCTGAGCCCCCCACCTCCTGCACATTGCACGCACGCACGCGCACACACACACACACACACACATGCCCCTGGCACGTGTCCACACGTGTGCACAGGTGTGTGCAGATACTCAGGGATGGAGCCGCTGCTGAGAGACTTGGGGGAAAGACTGGTCAACAAGGGCTGTTCTGGAAACTTCTCTCCAAGTAATCCACAGGCCTGACCGTAGGTGCTATGGGCACGGGGTCCCCTAGCCCAGGCTCTTAGTGACTCACGTCACCTCTCCCCAGCGGCCCGCTCCATCTGTGAAACACTGCAGCCCCTTCCTGGTGGCTCATCCATGCAGGACAGGGCATTTGCCCTGAGAGGCCGCCACTGTCCCCAAATCCAGCCTAGGAGTGCTGAC
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSBTAG00000014269_CASSETTE1
Average complexity
S*
Mappability confidence:
100%=100=100%
Protein Impact
Alternative protein isoforms (No Ref, Alt. Stop)
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.000 A=0.000 C2=0.103
Domain overlap (PFAM):
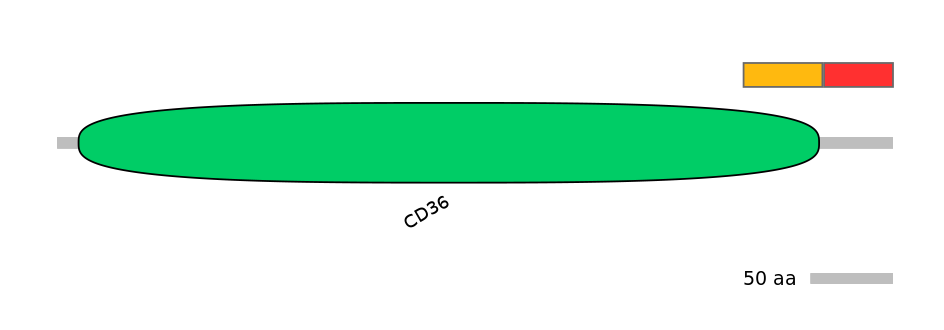
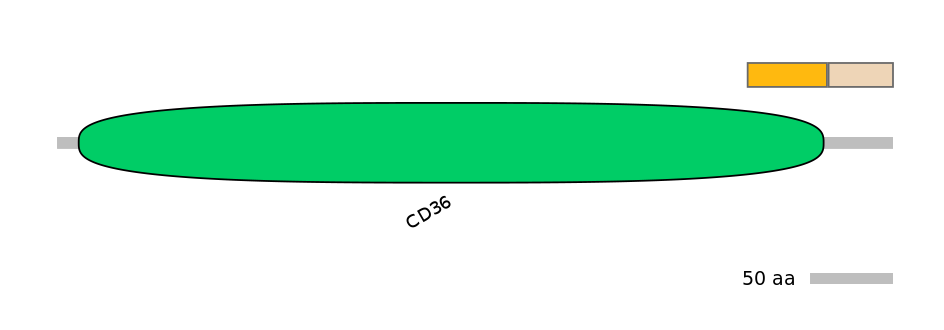
C1:
PF0113016=CD36=PD(10.2=93.9)
A:
NO
C2:
NO
Other Inclusion Isoforms:
NA
Other Skipping Isoforms:
NA
Associated events
Conservation
Chicken
(galGal4)
No conservation detected
Zebrafish
(danRer10)
No conservation detected
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
CAGTATGTGCTCCTTGCCCTG
R:
TGTGTGTGTGTGTGTGTGTGT
Band lengths:
247-376
Functional annotations
There are 6 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 14570588
This study identify several putative signalling motifs in the C-terminus of human SR-BII, which are absent from SR-BI, and hypothesize that these motifs interact with signalling molecules to mobilize stored cholesteryl esters and/or promote the efflux of intracellular free cholesterol. 'Pull-down' assays using a panel of tagged SH3 (Src homology 3) domains showed that cytoplasmic SR-BII, but not cytoplasmic SR-BI, bound the SH3 domain of phospholipase C-gamma1; this interaction was not, however, detected under more physiological conditions. Specific anti-peptide antisera identified SR-BII in human monocyte/macrophage THP-1 cells and, in recombinant cells, revealed receptor localization to caveolae, a plasma membrane microdomain that concentrates signal-transducer molecules and acts as a conduit for cholesterol flux between cells and lipoproteins. Consistent with its caveolar localization, expression of human SR-BII in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-SR-BII) was associated with increased HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux. Nevertheless, when CHO-SR-BII cells were pre-loaded with cholesteryl [(3)H]oleate and incubated with HDL, cholesteryl ester stores were not reduced compared with control cells.
PMID: 14726519
Whereas SR-BI was mainly ( approximately 70%) localized on the surface of transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells, as determined by biotinylation, HDL binding at 4 degrees C, and studies of enhanced green fluorescent protein-tagged SR-BI/II fusion proteins, the majority of SR-BII ( approximately 80-90%) was expressed intracellularly. The cellular distribution of SR-BI was not affected by deletion of the C terminus, which suggests that the distinct C terminus of SR-BII is responsible for its intracellular expression. Pulse-chase experiments showed that SR-BII rapidly internalized HDL protein, whereas in the case of SR-BI most HDL protein remained surface bound. Like its ligand, SR-BII was more rapidly endocytosed compared with SR-BI. Despite more rapid HDL uptake by SR-BII than SR-BI, selective cholesteryl ether uptake was significantly lower. Relative to their levels of expression at the cell surface, however, both isoforms mediated selective uptake with similar efficiency. HDL protein that was internalized by SR-BII largely co-localized with transferrin in the endosomal recycling compartment. Within the endosomal recycling compartment of SR-BII cells, there was extensive co-localization of internalized HDL lipid and protein. These results do not support a model that selective lipid uptake by SR-BI requires receptor/ligand recycling within the cell.
PMID: 17215280
HCV soluble E2 can interact with human SR-BI and SR-BII. Increased expression of SR-BI and SR-BII in the Huh-7.5 hepatoma cell line enhanced HCV strain J6/JFH and JFH infectivity, suggesting that endogenous levels of these receptors limit infection. Elevated expression of SR-BI, but not SR-BII, increased the rate of J6/JFH infection, which may reflect altered intracellular trafficking of the splice variants. In human plasma, HCV particles have been reported to be complexed with lipoproteins, suggesting an indirect interaction of the virus with SR-BI and other lipoprotein receptors. Plasma from J6/JFH-infected uPA-SCID mice transplanted with human hepatocytes demonstrates an increased infectivity for SR-BI/II-overexpressing Huh-7.5 cells.
PMID: 34097506
In this study, using human SR-BI (hSR-BI) and hSR-BII transgenic mice, the authors found that SR-BI and, to a lesser extent, its splicing variant SR-BII protect against LPS-induced lung damage. At 20 h after intratracheal LPS instillation, the extent of pulmonary inflammation and vascular leakage was significantly lower in hSR-BI and hSR-BII transgenic mice than in wild-type mice. Higher bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) inflammatory cell count and protein content and lung tissue neutrophil infiltration found in wild-type mice were associated with markedly (2 to 3 times) increased proinflammatory cytokine production compared to these parameters in transgenic mice following LPS administration. The markedly lower endotoxin levels detected in BALF of transgenic versus wild-type mice and the significantly increased BODIPY-LPS uptake observed in lungs of hSR-BI and hSR-BII mice 20 h after the i.t. LPS injection suggest that hSR-BI- and hSR-BII-mediated enhanced LPS clearance in the airways could represent the mechanism of their protective role against LPS-induced acute lung injury.
PMID: 9614139
Subcellular fractionation of transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells showed that SR-BII, like SR-BI, is enriched in caveolae, indicating that the altered cytoplasmic tail does not affect targeting of the receptor. SR-BII mediated both selective cellular uptake of cholesteryl ether from HDL as well as HDL-dependent cholesterol efflux from cells, although with approximately 4-fold lower efficiency than SR-BI. In vivo studies using adenoviral vectors showed that SR-BII was relatively less efficient than SR-BI in reducing plasma HDL cholesterol. These studies show that SR-BII, an HDL receptor isoform containing a distinctly different cytoplasmic tail, mediates selective lipid transfer between HDL and cells, but with a lower efficiency than the previously characterized variant.
PMID: 22749401
Inclusion decreases interaction with APOA1, but not with itself. By LUMIER.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- Pre-implantation embryo development