DreEX0040139 @ danRer10
Exon Skipping
Gene
ENSDARG00000071863 | itgb1a
Description
integrin, beta 1a [Source:ZFIN;Acc:ZDB-GENE-060803-2]
Coordinates
chr24:1116468-1123105:-
Coord C1 exon
chr24:1122939-1123105
Coord A exon
chr24:1119040-1119117
Coord C2 exon
chr24:1116468-1117307
Length
78 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
CTGTCCTTCTCCACTCTCAGACA
3' ss Score
9.49
5' ss Seq
TGAGTTTGT
5' ss Score
-5.25
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
AGTGTCCGCCGGGTCCAGATATCATCCCCATCGTGGCCGGTGTAGTGGCAGGAATCGTGCTGATCGGTCTCGCTCTGCTGCTCATCTGGAAGCTGCTCATGATCATCCACGACCGACGTGAATTCGCCAAATTCGAGAAGGAGAAGATGAACGCCAAGTGGGACACG
Seq A exon
ACAGAGAATCCAATTTACAAGAGCCCCATTAATAAATTCCAGAACCCAAACTATGGACGTAAAGCTGCGGCTCTATGA
Seq C2 exon
GGAGAAAACCCCATCTACAAGAGCGCCGTCACAACTGTGATCAACCCCAAATACGAAGGCAAATAATGGCCATCAGAATCACTCACCAGGATGTTTGGCAAGGGATGGGTGTGCGGATTTCCTCCCTATTTCTTTATTTTCTCATTCGTTTAGATCAATACTAGGAAGTTGTATTTCATGTCCGCCTCTCATCCCTTGCAAACCTGTACAGTCTGTATAGTCTTTTAACTTTCATTGGTTTTCCTTCTTTTACACCCTGTGCACATTCACGCAATCTCTCAATTCAGAACCGACAGATATCTGTGCCTTTGCATAAAGCTTTATATAAAAGGGATCCTTAAAAATCCAGACTTAGTGGAAATACAGGCCTACAGTATTGAAAAACATGCAATGCATTGCTCCAGGTACGTTTCGTTGTACGTTTCAGATGACAAATCCACTAGAGGGCGGAAGATTTTTGGAAATTTACATAAGTTAAGGCCACAGTGCAGTTAATTTTT
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSDARG00000071863_CASSETTE1
Average complexity
S
Mappability confidence:
100%=100=100%
Protein Impact
Alternative protein isoforms (No Ref, Alt. Stop)
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.000 A=0.000 C2=0.000
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF079657=Integrin_B_tail=PD(6.7=10.7),PF087256=Integrin_b_cyt=PU(53.2=44.6)
A:
PF087256=Integrin_b_cyt=PD(42.6=76.9)
C2:
PF087256=Integrin_b_cyt=PD(42.6=90.9)
Main Inclusion Isoform:
ENSDART00000039700fB3344
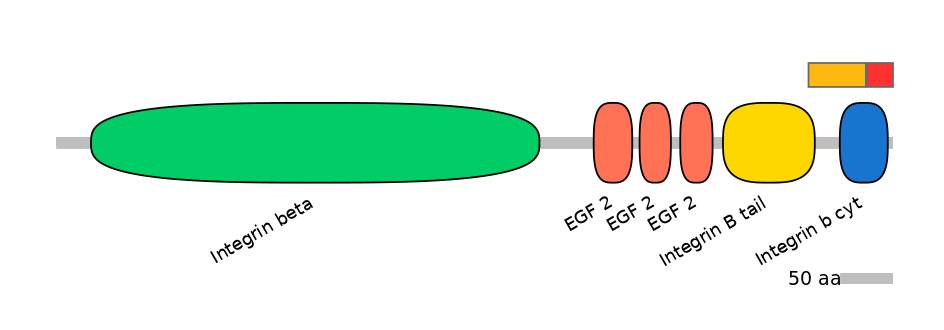
Other Inclusion Isoforms:
NA
Other Skipping Isoforms:
NA
Associated events
Conservation
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
GCTCATGATCATCCACGACCG
R:
ACCCATCCCTTGCCAAACATC
Band lengths:
183-261
Functional annotations
There are 4 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 9497328
Findings: 1) that both conformation and protein binding properties are altered by insertion of Gly spacers C-terminal to the heptad repeat sequences; 2) that the cytoskeletal proteins talin and filamin are among the polypeptides that bind to the integrin beta1A tail. Filamin, but not talin binding, is enhanced by the insertion of Gly spacers; 3) binding of both cytoskeletal proteins to beta1A is direct and specific, since it occurs with purified talin and filamin and is inhibited in a point mutant (beta1A(Y788A)) or in splice variants (beta1B, beta1C) known to disrupt cytoskeletal associations of beta1 integrins; 4) that the muscle-specific splice variant, beta1D (inclusion of HsaEX6088113), binds talin more tightly than beta1A and is therefore predicted to form more stable cytoskeletal associations; and 5) that the beta7 cytoplasmic domain binds filamin better than beta1A. Isof A: KLlmiihdrrefakfekekmnakwdtgenpiyksavttvvnpkyegk. Isof B: KLlmiihdrrefakfekekmnakwdtvsyktskkqsgl. Isof C: KLlmiihdrrefakfekekmnakwdtslsvaqpgvqwcdisslqpltsrfqqfsclslpstwdyrvkilfirvp. Isof D: KLlmiihdrrefakfekekmnakwdtqenpiykspinnfknpnygrkagl
PMID: 28560430
In vitro and in vivo experiments were designed to study the mechanism underlying the regulation of integrin B1 splicing by the Fyn/hnRNP E1 spliceosome. Expression of hnRNP E1 and integrin B1A (skipping form) were associated with metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Inhibition of Fyn activity upregulated the expression of P21-activated kinase 1 and promoted the phosphorylation and nuclear localization of hnRNP E1, leading to the construction of a spliceosome complex that affected the alterative splicing of integrin B1. In the hnRNP E1 spliceosome complex, hnRNP A1 and serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1 were responsible for binding to the pre-mRNA of integrin B1. Suppression of Fyn activity and/or overexpression of hnRNP E1 decreased the metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. In pancreatic cancer, the present study demonstrated a novel mechanism by which Fyn/hnRNP E1 signaling regulates pancreatic cancer metastasis by affecting the alternative splicing of integrin B1.
PMID: 9396762
Expression of muscle-specific beta1D integrin with an alternatively spliced cytoplasmic domain in CHO and GD25, beta1 integrin-minus cells leads to their phenotypic conversion. beta1D-transfected nonmuscle cells display rounded morphology, lack of pseudopodial activity, retarded spreading, reduced migration, and significantly enhanced contractility compared with their beta1A-expressing counterparts. The transfected beta1D is targeted to focal adhesions and efficiently displaces the endogenous beta1A and alphavbeta3 integrins from the sites of cell-matrix contact. This displacement is observed on several types of extracellular matrix substrata and leads to elevated stability of focal adhesions in beta1D transfectants. Whereas a significant part of cellular beta1A integrin is extractable in digitonin, the majority of the transfected beta1D is digitonin-insoluble and is strongly associated with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeleton. Increased interaction of beta1D integrin with the actin cytoskeleton is consistent with and might be mediated by its enhanced binding to talin. In contrast, beta1A interacts more strongly with alpha-actinin, than beta1D. Inside-out driven activation of the beta1D ectodomain increases ligand binding and fibronectin matrix assembly by beta1D transfectants. Phenotypic effects of beta1D integrin expression in nonmuscle cells are due to its enhanced interactions with both cytoskeletal and extracellular ligands. They parallel the transitions that muscle cells undergo during differentiation. Modulation of beta1 integrin adhesive function by alternative splicing serves as a physiological mechanism reinforcing the cytoskeleton- matrix link in muscle cells. This reflects the major role for beta1D integrin in muscle, where extremely stable association is required for contraction.
PMID: 9614138
The beta1 integrin subunit is widely expressed in vivo and is represented by four alternatively spliced cytoplasmic domain isoforms. beta1D is a muscle-specific variant of beta1 integrin and a predominant beta1 isoform in striated muscles. In the present study the authors showed that expression of the exogenous beta1D integrin in C2C12 myoblasts and NIH 3T3 or REF 52 fibroblasts inhibited cell proliferation. Unlike the case of the common beta1A isoform, adhesion of beta1D-transfected C2C12 myoblasts specifically via the expressed integrin did not activate mitogen-activated protein kinases. The beta1D-induced growth inhibitory signal was shown to occur late in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, before the G1-S transition. Ha-(12R)Ras, but not (Delta22W)Raf-1 oncogene, was able to overcome completely the beta1D-triggered cell growth arrest in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Since perturbation of the beta1D amino acid sequence in beta1A/beta1D chimeric integrins decreased the growth inhibitory signal, the entire cytoplasmic domain of beta1D appeared to be important for this function. However, an interleukin-2 receptor-beta1D chimera containing the cytoplasmic domain of beta1D still efficiently inhibited cell growth, showing that the ectodomain and the ligand-binding site in beta1D were not required for the growth inhibitory signal. Together, these data showed a new specific function for the alternatively spliced beta1D integrin isoform. Since the onset of beta1D expression during myodifferentiation coincides with the timing of myoblast withdrawal from the cell cycle, the growth inhibitory properties of beta1D demonstrated in this study might reflect the major function for this integrin in commitment of differentiating skeletal muscle cells in vivo.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]