DmeEX0005112 @ dm6
Exon Skipping
Gene
FBgn0264695 | Mhc
Description
The gene Myosin heavy chain is referred to in FlyBase by the symbol DmelMhc (CG17927, FBgn0264695). It is a protein_coding_gene from Dmel. It has 22 annotated transcripts and 22 polypeptides (20 unique). Gene sequence location is 2L:16766566..16788766. Its molecular function is described by 6 unique terms, many of which group under: nucleoside-triphosphatase activity; catalytic activity; hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides; drug binding; actin filament binding. It is involved in the biological process described with 15 unique terms, many of which group under: epithelial cell development; adult somatic muscle development; regulation of biological quality; reproductive process; protein stabilization. 161 alleles are reported. The phenotypes of these alleles manifest in: somatic cell of ovariole; muscle attachment site; embryonic/larval heart; adult visceral muscle; germline cell. The phenotypic classes of alleles include: sterile; fertile; phenotype; increased mortality during development.
Coordinates
chr2L:16776850-16780813:+
Coord C1 exon
chr2L:16776850-16777439
Coord A exon
chr2L:16777631-16777748
Coord C2 exon
chr2L:16780550-16780813
Length
118 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
ATTGTAATACTCAACTATAGTTA
3' ss Score
2.58
5' ss Seq
AAGGCACGC
5' ss Score
2.65
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
TTGGGCAAGTCGGCTCCATTCCAGAAGCCCAAGCCTCCAAAGCCCGGTCAGCAGGCTGCCCACTTCGCCATTGCCCATTATGCTGGTTGTGTGTCCTACAACATCACCGGTTGGTTGGAGAAGAACAAGGATCCTCTGAACGACACCGTTGTCGACCAGTTCAAGAAGTCGCAGAACAAGCTGCTGATCGAAATCTTCGCCGATCACGCCGGTCAGTCGGGTGGCGGTGAACAGGCCAAGGGAGGTCGTGGCAAGAAGGGCGGTGGCTTCGCTACCGTCTCGTCGGCCTACAAGGAGCAGTTGAACAGCTTGATGACCACTCTGCGTTCGACCCAGCCTCACTTCGTCCGTTGCATCATTCCCAACGAAATGAAGCAGCCTGGCGTGGTTGATGCCCACTTGGTCATGCACCAGCTGACCTGTAACGGTGTGCTTGAAGGTATCCGTATTTGCCGTAAGGGCTTCCCCAACAGGATGATGTACCCTGACTTCAAGATGCG
Seq A exon
TTACATGATTCTGGCTCCTGCCATCATGGCGGCCGAAAAGGTGGCCAAGAATGCTGCCGGAAAGTGCTTGGAAGCCGTCGGACTGGATCCCGATATGTACCGCATTGGTCACACCAAG
Seq C2 exon
GTGTTCTTCCGCGCCGGTGTCCTGGGTCAGATGGAGGAGTTCCGTGATGAGCGTCTGGGCAAGATCATGTCCTGGATGCAGGCATGGGCCCGTGGTTACCTGTCCCGTAAGGGCTTCAAGAAGCTCCAGGAACAGCGCGTCGCCCTCAAGGTTGTCCAGCGCAATCTGCGCAAGTACCTGCAGCTCCGTACCTGGCCCTGGTACAAACTGTGGCAGAAGGTCAAGCCCCTCCTCAACGTCAGCCGCATCGAGGATGAGATTGCC
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
FBgn0264695_MULTIEX1-1/6=C1-6
Average complexity
ME(1-2[100=100];1-3[100=100];1-5[100=100])
Mappability confidence:
100%=100=83%
Protein Impact
ORF disruption upon sequence inclusion
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.177 A=0.000 C2=0.000
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF0006316=Myosin_head=FE(28.9=100)
A:
PF0006316=Myosin_head=FE(5.8=100)
C2:
PF0006316=Myosin_head=PD(0.4=3.4),PF0061222=IQ=WD(100=23.9)
Main Inclusion Isoform:
FBpp0298830
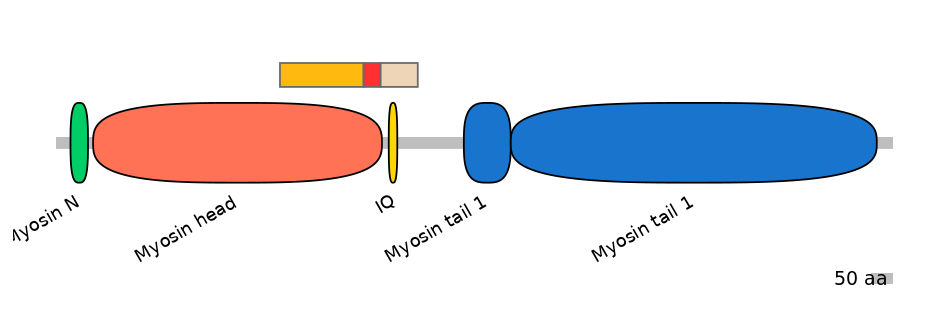
Main Skipping Isoform:
FBpp0080452
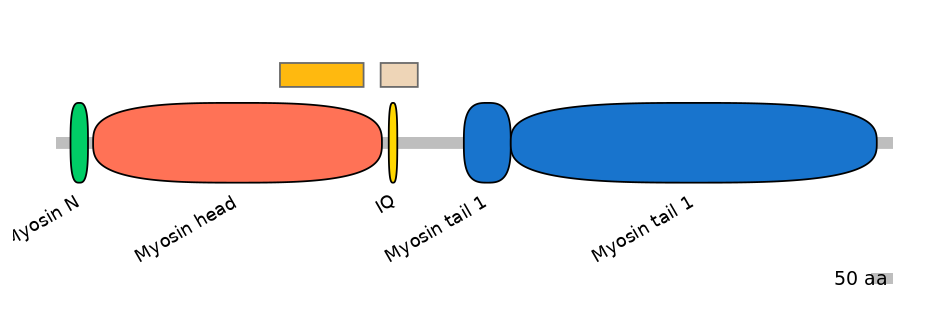
Other Inclusion Isoforms:
FBpp0080463
Other Skipping Isoforms:
FBpp0080453, FBpp0080454, FBpp0080455, FBpp0080456, FBpp0080457, FBpp0080458, FBpp0080459, FBpp0080460, FBpp0080462, FBpp0080464, FBpp0291041, FBpp0291042, FBpp0291043, FBpp0298827, FBpp0298828, FBpp0298829, FBpp0298831, FBpp0312323
Associated events
Conservation
Human
(hg38)
No conservation detected
Human
(hg19)
No conservation detected
Mouse
(mm10)
No conservation detected
Mouse
(mm9)
No conservation detected
Rat
(rn6)
No conservation detected
Cow
(bosTau6)
No conservation detected
Chicken
(galGal4)
No conservation detected
Chicken
(galGal3)
No conservation detected
Zebrafish
(danRer10)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
TTGATGACCACTCTGCGTTCG
R:
CAGACGCTCATCACGGAACTC
Band lengths:
248-366
Functional annotations
There are 3 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 24115062
This event
Replacing the endogenous converter with an embryonic version decreased SA tension and the rate of SA tension generation. The alterations in SA properties and myosin kinetics from the converter exchange caused power generation to drop to 10% of control fiber power when the optimal conditions for control fibers - 1% muscle length (ML) amplitude and 150 Hz oscillation frequency - were applied to fibers expressing the embryonic converter (IFI-EC). Optimizing conditions for IFI-EC fiber power production, by doubling ML amplitude and decreasing oscillation frequency by 60%, improved power output to 60% of optimized control fiber power. IFI-EC flies altered their aerodynamic flight characteristics to better match optimal fiber power generation conditions as wing beat frequency decreased and wing stroke amplitude increased. This enabled flight in spite of the drastic changes to fiber mechanical performance. IFI isoform: DmeEX0005112; EMB: DmeEX0005115
PMID: 29539400
This event
The authors studied the influence of the converter, a myosin structural region at the junction of the lever arm and catalytic domain, using Drosophila because its single myosin heavy chain gene expresses five alternative converter versions (11a-e; DmeEX0005112-6). the authors created five transgenic fly lines, each forced to express one of the converter versions in their indirect flight muscle (IFM) fibers. Electron microscopy showed that the converter exchanges did not alter muscle ultrastructure. The four lines expressing converter versions (11b-e) other than the native IFM 11a converter displayed decreased flight ability. IFM fibers expressing converters normally found in the adult stage muscles generated up to 2.8-fold more power and displayed up to 2.2-fold faster muscle kinetics than fibers with converters found in the embryonic and larval stage muscles. Small changes to stretch-activated force generation only played a minor role in altering power output of IFM. Muscle apparent rate constants, derived from sinusoidal analysis of the chimeric converter fibers, showed a strong positive correlation between optimal muscle oscillation frequency and myosin attachment kinetics to actin, and an inverse correlation with detachment related cross-bridge kinetics. This suggests the myosin converter alters at least two rate constants of the cross-bridge cycle with changes to attachment and power stroke related kinetics having the most influence on setting muscle oscillatory power kinetics.
PMID: 30865518
This event
The authors measured FVR properties of Drosophila jump muscle fibers from five transgenic lines each expressing a single converter. Consistent with the hypothesis, the authors observed up to 2.4-fold alterations in FVR curvature. Maximum shortening velocity (v0) and optimal velocity for maximum power generation were also altered, but isometric tension and maximum power generation were unaltered. Converter 11a, normally found in the indirect flight muscle (IFM), imparted the highest FVR curvature and v0, whereas converter 11d, found in larval body wall muscle, imparted the most linear FVR and slowest v0. Jump distance strongly correlated with increasing FVR curvature and v0, meaning flies expressing the converter from the IFM jumped farther than flies expressing the native jump muscle converter. Fitting the data with Huxley's two-state model and a biophysically based four-state model suggest a testable hypothesis that the converter sets muscle type FVR curvature by influencing the detachment rate of negatively strained myosin via changes in the force dependence of product release.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- Neural diversity
- Neurogenesis
- Neuronal activity
- Splicing factor regulation (brain)
- Splicing factor regulation (SL2)