HsaEX0003152 @ hg19
Exon Skipping
Gene
ENSG00000188157 | AGRN
Description
agrin [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:329]
Coordinates
chr1:987108-989357:+
Coord C1 exon
chr1:987108-987195
Coord A exon
chr1:988841-988873
Coord C2 exon
chr1:989133-989357
Length
33 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
CCTCTCTTCCTGCTTCTAAGCCC
3' ss Score
5.57
5' ss Seq
CAGGTGAGC
5' ss Score
9.6
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
GGCTGGTGGAGAAGTCAGCGGGGGACGTGGATACCTTGGCCTTTGACGGGCGGACCTTTGTCGAGTACCTCAACGCTGTGACCGAGAG
Seq A exon
CCCCGAAACTCTGGATTCCGGGGCCCTTCACAG
Seq C2 exon
CGAGAAGGCACTGCAGAGCAACCACTTTGAACTGAGCCTGCGCACTGAGGCCACGCAGGGGCTGGTGCTCTGGAGTGGCAAGGCCACGGAGCGGGCAGACTATGTGGCACTGGCCATTGTGGACGGGCACCTGCAACTGAGCTACAACCTGGGCTCCCAGCCCGTGGTGCTGCGTTCCACCGTGCCCGTCAACACCAACCGCTGGTTGCGGGTCGTGGCACATAG
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSG00000188157-'44-48,'44-47,46-48
Average complexity
S
Mappability confidence:
100%=80=100%
Protein Impact
Alternative protein isoforms (No Ref)
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.000 A=0.391 C2=0.006
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
NO
A:
NO
C2:
PF0005418=Laminin_G_1=PU(47.0=81.6)
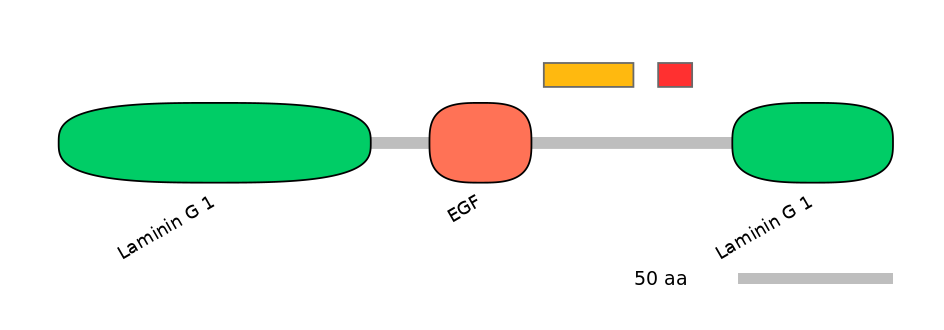
Other Inclusion Isoforms:
NA
Other Skipping Isoforms:
NA
Associated events
Other assemblies
Conservation
Chicken
(galGal3)
No conservation detected
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
GTCGAGTACCTCAACGCTGTG
R:
CCTTGCCACTCCAGAGCAC
Band lengths:
112-145
Functional annotations
There are 6 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 8026466
This event
In the experiments reported here the authors investigate the regions of agrin necessary for nAChR clustering activity using two different methods. First, the authors expressed truncated soluble forms of the agrin protein in mammalian cells and assessed their clustering activity. Second, the authors generated a panel of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against agrin and mapped their epitopes. Several mAbs block agrin-induced aggregation of nAChRs. One of the mAbs, Agr86, binds exclusively to the CNS-specific splicing variants and thus identifies an epitope common only to these more active isoforms. Mapping of the Agr86 epitope suggests that alternative splicing results in a distributed conformational change in the agrin protein. Taken together these data suggest that four domains in the C-terminal 55 kDa of agrin contribute to its nAChR clustering activity.
PMID: 8625852
This event
Agrin is a component of the extracellular matrix that regulates aspects of neuromuscular junction differentiation. Identification of agrin-binding proteins has lead to the suggestion that alpha-dystroglycan is a muscle cell surface proteoglycan that mediates agrin activity. To further test this hypothesis, the authors have compared the ability of differentially active agrin isoforms to interact with a model component of proteoglycans, heparin, as well as with the putative proteoglycan alpha-dystroglycan. The authors demonstrate that an alternately spliced exon (encoding the sequence lysine, serine, arginine, lysine: Y site) (HsaEX0003154) is necessary for agrin-heparin interactions. The authors also show that alternate splicing at another site (Z site) (HsaEX0003157) dramatically affects interaction of alpha-dystroglycan with agrin. A bigger Z-site insert (inclusion of both HsaEX003157 and HsaEX0003152) shows that it is only the HsaEX0003157 insert that affects the alpha-dystroglycan interaction. None of the exons in the Z-site insert appears to affect the heparain binding.
PMID: 17012237
This event
Overexpression of A4B11 and A4B8, but not A0B0 or A4B0, induces MuSK phosphorylation activity. The conserved tripeptide asparagineglutamate-isoleucine in the eight-amino acid long insert at the B-site (HsaEX0003157) is necessary and sufficient for full MuSK phosphorylation activity. However, even if all eight amino acids were replaced by alanines, this agrin mutant still has significantly higher MuSK phosphorylation activity than the splice version lacking any insert. The study also shows that binding to alpha-dystroglycan requires at least two LG domains and that amino acid inserts at the A and the B splice sites negatively affect binding. A4 = HsaEX0003154, B8 = HsaEX0003157, B11 = HsaEX0003152.
PMID: 7860635
Alternative splicing of chick agrin mRNA at two sites, A (GgaEX0002487) and B (GgaEX1007051 and GgaEX1007055), gives rise to eight possible isoforms of which five are expressed in vivo. Motor neurons express high levels of isoforms with inserts at sites A and B, muscle cells synthesize isoforms that lack amino acids at the B-site. To obtain further insights into the mechanism of agrin-induced AChR aggregation, the authors determined the EC50 (effective concentration to induce half-maximal AChR clustering) of each agrin isoform and of truncation mutants. On chick myotubes, EC50 of the COOH-terminal, 95-kD fragment of agrinA4B8 was approximately 35 pM, of agrinA4B19 approximately 110 pM and of agrinA4B11 approximately 5 nM. While some AChR clusters were observed with 64 nM of agrinA4B0, no activity was detected for agrinA0B0. Recombinant full-length chick agrin and a 100-kD fragment of ray agrin showed similar EC50 values. A 45-kD, COOH-terminal fragment of agrinA4B8 retained high activity (EC50 approximately equal to 130 pM) and a 21-kD fragment was still active, but required higher concentrations (EC50 approximately equal to 13 nM). Unlike the 45-kD fragment, the 21-kD fragment neither bound to heparin nor did heparin inhibit its capability to induce AChR aggregation. These data show quantitatively that agrinA4B8 and agrinA4B19, expressed in motor neurons, are most active, while no activity is detected in agrinA0B0, the dominant isoform synthesized by muscle cells. A4 = HsaEX0003154/GgaEX0002487, B8 = HsaEX0003157, B11 = HsaEX0003152/GgaEX1007055, B19= HsaEX0003152/GgaEX1007055+HsaEX0003157.
PMID: 8398142
Neural agrin, an extracellular matrix protein secreted by motor neurons, plays a key role in clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) on postsynaptic membranes of the neuromuscular junction. The insertion of this exon (11aa) at the z site has much less importance for AChR clustering than HsaEX0003157.
PMID: 10402191
Multiple alternatively spliced forms of agrin that differ in binding characteristics and bioactivity are synthesized by nerve and muscle cells. The authors used surgical chimeras, isoform-specific mutant mice, and nerve-muscle cocultures to determine the origins and nature of the agrin required for synaptogenesis. The authors show that agrin containing Z exons (Z+) is a critical nerve-derived inducer of postsynaptic differentiation, whereas neural isoforms containing a heparin binding site (Y+) and all muscle-derived isoforms are dispensable for major steps in synaptogenesis. These results also suggest that the requirement of agrin for presynaptic differentiation is mediated indirectly by its ability to promote postsynaptic production or localization of appropriate retrograde signals.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)
- Genotype-Tissue Expression Project (GTEx)
- Autistic and control brains
- Pre-implantation embryo development
Other AS DBs:
FasterDB (Includes CLIP-seq data)
AS-ALPS (AS-induced ALteration of Protein Structure, links to PINs)
APPRIS (Selection of principal isoform)
DEU primates (Only for human)