HsaEX0032370 @ hg19
Exon Skipping
Gene
ENSG00000091409 | ITGA6
Description
integrin, alpha 6 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:6142]
Coordinates
chr2:173362703-173371002:+
Coord C1 exon
chr2:173362703-173362828
Coord A exon
chr2:173366500-173366629
Coord C2 exon
chr2:173368819-173371002
Length
130 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
AATACCTTGCTTCCTTGTAGTGT
3' ss Score
7.39
5' ss Seq
TTGGTAATT
5' ss Score
5.73
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
GTTCGAGTGACTGTGTTTCCCTCAAAGACTGTAGCTCAGTATTCGGGAGTACCTTGGTGGATCATCCTAGTGGCTATTCTCGCTGGGATCTTGATGCTTGCTTTATTAGTGTTTATACTATGGAAG
Seq A exon
TGTGGTTTCTTCAAGAGAAATAAGAAAGATCATTATGATGCCACATATCACAAGGCTGAGATCCATGCTCAGCCATCTGATAAAGAGAGGCTTACTTCTGATGCATAGTATTGATCTACTTCTGTAATTG
Seq C2 exon
TGTGGATTCTTTAAACGCTCTAGGTACGATGACAGTGTTCCCCGATACCATGCTGTAAGGATCCGGAAAGAAGAGCGAGAGATCAAAGATGAAAAGTATATTGATAACCTTGAAAAAAAACAGTGGATCACAAAGTGGAACGAAAATGAAAGCTACTCATAGCGGGGGCCTAAAAAAAAAAAGCTTCACAGTACCCAAACTGCTTTTTCCAACTCAGAAATTCAATTTGGATTTAAAAGCCTGCTCAATCCCTGAGGACTGATTTCAGAGTGACTACACACAGTACGAACCTACAGTTTTAACTGTGGATATTGTTACGTAGCCTAAGGCTCCTGTTTTGCACAGCCAAATTTAAAACTGTTGGAATGGATTTTTCTTTAACTGCCGTAATTTAACTTTCTGGGTTGCCTTTATTTTTGGCGTGGCTGACTTACATCATGTGTTGGGGAAGGGCCTGCCCAGTTGCACTCAGGTGACATCCTCCAGATAGTGTAGCTGAG
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSG00000091409_CASSETTE2
Average complexity
S
Mappability confidence:
100%=100=100%
Protein Impact
Alternative protein isoforms (No Ref, Alt. Stop)
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.000 A=0.114 C2=0.000
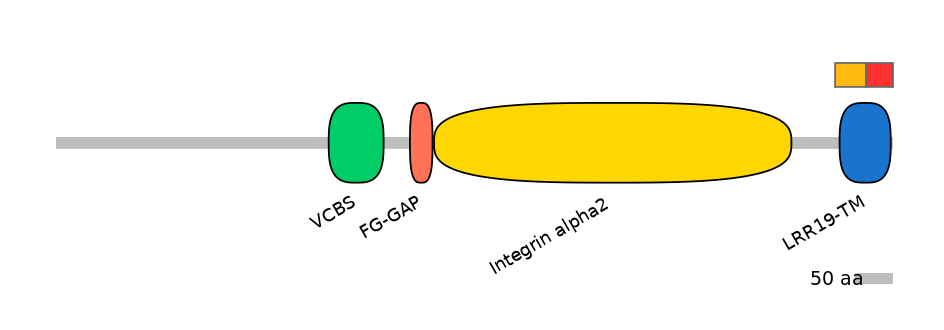
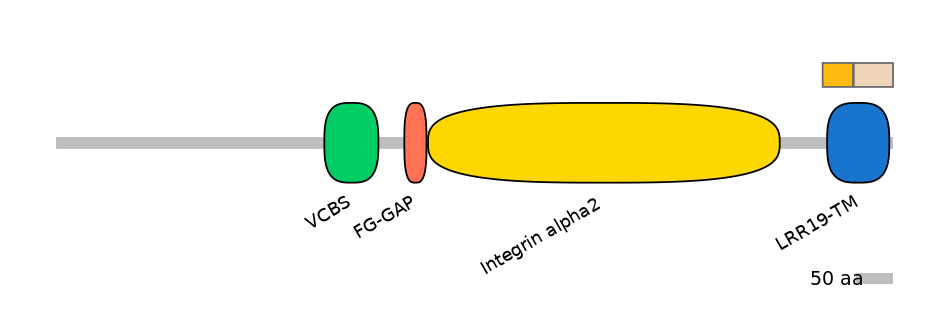
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF052976=Herpes_LMP1=PU(53.6=88.1),PF151761=LRR19-TM=PU(41.4=85.7),PF0035715=Integrin_alpha=PU(0.1=0.0)
A:
PF151761=LRR19-TM=PD(46.4=88.9),PF0035715=Integrin_alpha=PD(86.7=36.1)
C2:
PF052976=Herpes_LMP1=PD(43.5=55.6),PF151761=LRR19-TM=PD(56.3=90.7),PF0035715=Integrin_alpha=PD(83.3=18.5)
Associated events
Other assemblies
Conservation
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
TCGGGAGTACCTTGGTGGATC
R:
TTAGGCCCCCGCTATGAGTAG
Band lengths:
257-387
Functional annotations
There are 11 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 7681434
This event
This study demonstrates that integrin alpha 6A (includes penultimate exon (HsaEX0032370)), but not integrin alpha 6B (skips penultimate exon), is a major target for PMA-induced phosphorylation. Phosphorylated integrin alpha 6A contained phosphoserine and a small amount of phosphotyrosine.
PMID: 10094488
This event
Two-yeast hybrid assay was used to examine interaction between various alpha integrins (including splice isoforms of integrin alpha 3 (alpha3A and alpha3B (these differ in presence of penultimae exon HsaEX0032352 (present in A, absent in B)), splice isoforms of integrin alpha 6 (alpha6A and alpha6B) (these differ in the presence of penultimate exon HsaEX0032370 (present in A, absent in B), and splice isoforms of integrin alpha 7 (alpha7A and alpha7B (these differ in presence of penultimate exon HsaEX0032377 (present in A, absent in B)) and four proteins, two of which are described as clones as they were identified in a cDNA screen (Mss4, BIN1, clone 63, and clone 80).
PMID: 10694445
This event
HEK293 overexpressing integrin alpha 6 isoforms alpha6A (contains penultimate exon (HsaEX0032370)) or alpha6B (lacks penultimate exon) are shown to adhere to similar extends to laminin-1, a fragment of laminin-1, and laminin-2. Migration across surfaces with above mentioned laminins is also similar. Negative results.
PMID: 11479315
This event
Both splice variants of alpha6integrin (alpha6A (includes penultimate exon (HsaEX0032370)) and alpha6B (lacks penultimate exon)) contain a conserved PDZ binding site that enables interaction with TIP-2/GIPC. The binding site in alpha6B defines a new subclass of type I PDZ interaction site, characterized by a non-aliphatic residue at position 0. Negative results
PMID: 11852236
This event
Different cDNA libraries were screened by the yeast two-hybrid system using as a bait the cytoplasmic sequence of integrin alpha6A or alpha6B subunits. Surprisingly, the same PDZ domain-containing protein, TIP-2/GIPC, was isolated with either of the variants, although their sequences are different. Direct interaction assays with the cytoplasmic domain of the integrin alpha1?7 subunits revealed that in addition to alpha6A (contains penultimate exon (HsaEX0032370)) and alpha6B (lacks penultimate exon), TIP-2/GIPC reacted also with alpha5, but not other alpha integrin subunits. The specificity of the interaction was confirmed by in vitro protein binding assays with purified peptides corresponding to integrin cytoplasmic domains. Further analysis with either truncation fragments of TIP-2/GIPC or mutated integrin cytoplasmic domains indicated that the interaction occurs between the PDZ domain of TIP-2/GIPC and a consensus PDZ domain-binding sequence, SDA, present at the C-terminus of the integrin alpha5 and alpha6A subunits. The integrin alpha6B subunit terminates with a different sequence, SYS, which may represent a new PDZ domain-binding motif. Negative results.
PMID: 24403311
This event
To investigate the functional significance of an alpha6A up-regulation in CRC, the authors specifically knocked down its expression in well-established CRC cell lines using a small-hairpin RNA approach. Results showed a growth rate reduction in all alpha6A knockdown CRC cell lines studied. The alpha6A silencing was also found to be associated with a significant repression of a number of Wnt/B-catenin pathway end points. Moreover, it was accompanied by a reduction in the capacity of these cells to develop tumours in xenografts. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the alpha6A variant is a pro-proliferative form of the alpha6 integrin subunit in CRC cells and appears to mediate its effects through the Wnt/B-catenin pathway. Note: function of a6A and a6B are compared directly.
PMID: 25561492
This event
The authors report that breast CSCs produce a laminin (LM) 511 matrix that promotes self-renewal and tumor initiation by engaging the alpha6Bbeta1 (lacks penultimate exon, HsaEX0032370) integrin (but not the alpha6Abeta1 integrin (contains penultimate exon) and activating the Hippo transducer TAZ. Although TAZ is important for the function of breast CSCs, the mechanism is unknown. The authors observed that TAZ regulates the transcription of the alpha5 subunit of LM511 and the formation of a LM511 matrix. These data establish a positive feedback loop involving TAZ and LM511 that contributes to stemness in breast cancer.
PMID: 7559532
Integrin receptors can mediate transmembrane signaling in response to ligand binding. To further examine the role of the integrin alpha subunit in these signaling functions, the authors assessed the contribution of the alpha 6 cytoplasmic domain variants to the signaling properties of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin using P388D1 cells that had been transfected with either the alpha 6A (includes penultimate exon (HsaEX0032370)) or the alpha 6B (lacks penultimate exon) cDNA. The alpha 6A beta 1 and alpha 6B beta 1 receptors induced marked quantitative differences in the tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins after binding to laminin. Specifically, the alpha 6A cytoplasmic domain was more effective than the alpha 6B cytoplasmic domain in inducing the tyrosine phosphorylation of three major proteins (molecular mass, 120, 110, and 76 kDa). In addition to these proteins, the authors also observed that the tyrosine phosphorylation of the cytoskeletal protein paxillin was increased significantly more by alpha 6A beta 1 integrin-mediated adhesion to laminin than by that of alpha 6B beta 1. This differential pattern of tyrosine phosphorylation induction does not appear to be a secondary event initiated by cell shape changes. Also, differences in tyrosine phosphorylation in the alpha 6 transfectants were not evident in response to attachment to other substrates.
PMID: 7949424
In the present study, the authors examined the possibility that the A (includes penultimate exon, HsaEX0032370) and B (lacks penultimate exon) variants of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin laminin receptor differ in function. For this purpose, the authors expressed the alpha 6A and alpha 6B cDNAs, as well as a truncated alpha 6 cDNA (alpha 6-delta CYT) in which the cytoplasmic domain sequence was deleted after the GFFKR pentapeptide, in P388D1 cells, an alpha 6 deficient macrophage cell line. Populations of stable alpha 6A, alpha 6B, and alpha 6-delta CYT transfectants that expressed equivalent levels of cell surface alpha 6 were obtained by fluorescence-activated cell sorter and shown to form heterodimers with endogenous beta 1 subunits. Upon attachment to laminin, the alpha 6A transfectants extended numerous pseudopodia. In contrast, the alpha 6B transfectants remained rounded and extended few processes. The transfectants were also examined for their ability to migrate toward a laminin substratum using Transwell chambers. The alpha 6A transfectants were three- to fourfold more migratory than the alpha 6B transfectants. The alpha 6-delta CYT transfectants did not attach to laminin in normal culture medium, but they did attach in the presence of Mn2+. The alpha 6-delta CYT transfectants migrated to a lesser extent than either the alpha 6A or alpha 6B transfectants in the presence of Mn2+. The alpha 6 transfectants differed significantly in the concentration of substratum bound laminin required for half-maximal adhesion in the presence of Mn2+:alpha 6A (2.1 micrograms/ml), alpha 6B (6.3 micrograms/ml), and alpha 6-delta CYT (8.8 micrograms/ml). Divalent cation titration studies revealed that these transfectants also differed significantly in both the [Ca2+] and [Mn2+] required to obtain half-maximal adhesion to laminin. These data demonstrate that the A and B variants of the alpha 6 cytoplasmic domain can differentially modulate the function of the alpha 6 beta 1 extracellular domain.
PMID: 9488728
The authors examined the possibility that the alpha6A (includes penultimate exon (HsaEX0032370)) and alpha6B (lacks penultimate exon) cytoplasmic domain variants of the alpha6beta1 integrin differentially activate p42 and p44 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases. P388D1 macrophages that express equivalent surface levels of either the alpha6Abeta1 or alpha6Bbeta1 integrin were used to examine this issue. Adhesion to laminin-1 mediated by the alpha6Abeta1 integrin triggered activation of a substantial fraction of total p42 and p44 MAP kinases as assessed using a mobility shift assay, immunoblot analysis with a phosphospecific MAP kinase antibody, and an immune complex kinase assay. In contrast, ligation of the alpha6Bbeta1 integrin did not trigger significant MAP kinase activation. These data were confirmed by antibody clustering of the alpha6beta1 integrins. Both the alpha6Abeta1 and alpha6Bbeta1 integrins were capable of activating the p70 ribosomal S6 kinase and this activation, unlike MAP kinase activation, is dependent on phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase. Activation of MAP kinase by alpha6beta1 requires both Ras and protein kinase C activity. A functional correlate for differential activation of MAP kinase was provided by the findings that the alpha6Abeta1 transfectants migrated significantly better on laminin than the alpha6Bbeta1transfectants and this migration was dependent on MAP kinase activity based on the use of the MAP kinase kinase (MEK1) inhibitor PD98059.
PMID: 24767994
Although the alpha6beta1 integrin has been implicated in the function of breast and other cancer stem cells (CSCs), little is known about its regulation and relationship to mechanisms involved in the genesis of CSCs. The authors report that a CD44high/CD24low population, enriched for CSCs, is comprised of distinct epithelial and mesenchymal populations that differ in expression of the two alpha6 cytoplasmic domain splice variants: alpha6A and alpha6B. alpha6Bbeta1 expression defines the mesenchymal population (tumor-initiating potential is much higher alpha6B isoform) and is necessary for CSC function, a function that cannot be executed by alpha6A integrins. The generation of alpha6Bbeta1 is tightly controlled and occurs as a consequence of an autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling that culminates in the transcriptional repression of a key RNA-splicing factor.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)
- Genotype-Tissue Expression Project (GTEx)
- Autistic and control brains
- Pre-implantation embryo development
Other AS DBs:
FasterDB (Includes CLIP-seq data)
AS-ALPS (AS-induced ALteration of Protein Structure, links to PINs)
APPRIS (Selection of principal isoform)
DEU primates (Only for human)