HsaEX0056556 @ hg38
Exon Skipping
Gene
ENSG00000183873 | SCN5A
Description
sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 5 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:10593]
Coordinates
chr3:38576661-38581371:-
Coord C1 exon
chr3:38580931-38581371
Coord A exon
chr3:38579334-38579492
Coord C2 exon
chr3:38576661-38576781
Length
159 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
GGCTGGGGTCTTTTCAGCAGGAA
3' ss Score
5.05
5' ss Seq
GAGGTAATG
5' ss Score
8.73
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
GTCCTGAATCTCTTCCTGGCCTTGCTGCTCAGCTCCTTCAGTGCAGACAACCTCACAGCCCCTGATGAGGACAGAGAGATGAACAACCTCCAGCTGGCCCTGGCCCGCATCCAGAGGGGCCTGCGCTTTGTCAAGCGGACCACCTGGGATTTCTGCTGTGGTCTCCTGCGGCAGCGGCCTCAGAAGCCCGCAGCCCTTGCCGCCCAGGGCCAGCTGCCCAGCTGCATTGCCACCCCCTACTCCCCGCCACCCCCAGAGACGGAGAAGGTGCCTCCCACCCGCAAGGAAACACGGTTTGAGGAAGGCGAGCAACCAGGCCAGGGCACCCCCGGGGATCCAGAGCCCGTGTGTGTGCCCATCGCTGTGGCCGAGTCAGACACAGATGACCAAGAAGAAGATGAGGAGAACAGCCTGGGCACGGAGGAGGAGTCCAGCAAGCAG
Seq A exon
GAATCCCAGCCTGTGTCCGGTGGCCCAGAGGCCCCTCCGGATTCCAGGACCTGGAGCCAGGTGTCAGCGACTGCCTCCTCTGAGGCCGAGGCCAGTGCATCTCAGGCCGACTGGCGGCAGCAGTGGAAAGCGGAACCCCAGGCCCCAGGGTGCGGTGAG
Seq C2 exon
ACCCCAGAGGACAGTTGCTCCGAGGGCAGCACAGCAGACATGACCAACACCGCTGAGCTCCTGGAGCAGATCCCTGACCTCGGCCAGGATGTCAAGGACCCAGAGGACTGCTTCACTGAAG
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSG00000183873_CASSETTE2
Average complexity
S*
Mappability confidence:
100%=100=100%
Protein Impact
Alternative protein isoforms (Ref)
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.524 A=1.000 C2=0.666
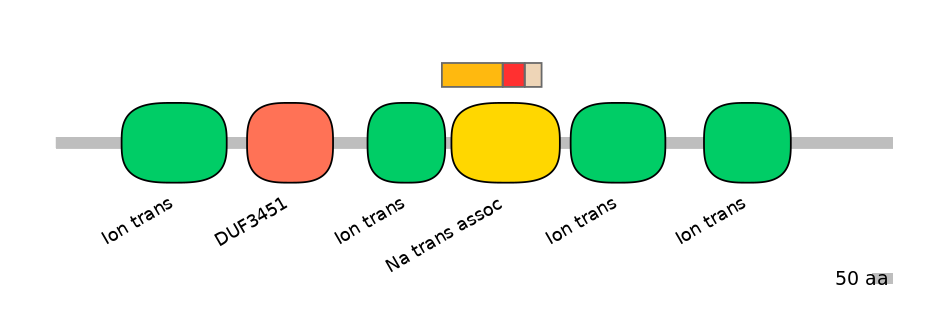
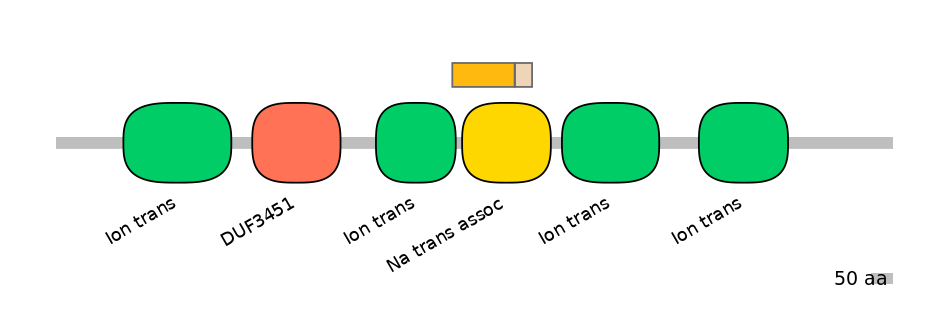
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF0052026=Ion_trans=PD(4.3=5.4),PF065128=Na_trans_assoc=PU(46.8=83.7)
A:
PF065128=Na_trans_assoc=FE(19.8=100)
C2:
PF065128=Na_trans_assoc=FE(15.2=100)
Other Inclusion Isoforms:
Associated events
Other assemblies
Conservation
Chicken
(galGal4)
No conservation detected
Chicken
(galGal3)
No conservation detected
Zebrafish
(danRer10)
No conservation detected
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
CGCAAGGAAACACGGTTTGAG
R:
GAGGTCAGGGATCTGCTCCAG
Band lengths:
243-402
Functional annotations
There are 1 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 21552533
Negative results. Nine Nav1.5 (SCN5A) splice variants are known. Four of them, namely Nav1.5a, Nav1.5c, Nav1.5d, and Nav1.5e, generate functional channels in heterologous expression systems. In the present study, the authors systematically investigated electrophysiological properties of mutant T1620K channels in the background of all known functional Nav1.5 splice variants in HEK293 cells. This mutation is associated with two cardiac excitation disorders: long QT syndrome type 3 (LQT3) and isolated cardiac conduction disease (CCD). When investigating the effect of the T1620K mutation, the authors noticed similar channel defects in the background of hNav1.5, hNav1.5a, and hNav1.5c. In contrast, the hNav1.5d background produced differential effects: In the mutant channel, some gain-of-function features did not emerge, whereas loss-of-function became more pronounced. In case of hNav1.5e, the neonatal variant of hNav1.5, both the splice variant itself as well as the corresponding mutant channel showed electrophysiological properties that were distinct from the wild-type and mutant reference channels, hNav1.5 and T1620K, respectively. In conclusion, these data show that alternative splicing is a mechanism capable of generating a variety of functionally distinct wild-type and mutant hNav1.5 channels. Thus, the cellular splicing machinery is a potential player affecting genotype-phenotype correlations in SCN5A channelopathies. (About variants: Variant a and c differs from the canonical variant by skipping exon 18 (HsaEX0056556), and including Q1077 (HsaALTA0007521-2/2), respectively. Negative results for those. Variant D seems to use alternative splice sites in exon 17 (not in VastDB), and variant E uses the neonatal version of the ME exon (HsaEX0056558), while the other variants use the adult version (HsaEX0056559)).
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- Genotype-Tissue Expression Project (GTEx)
- Autistic and control brains
- Pre-implantation embryo development