MmuEX0012269 @ mm9
Exon Skipping
Gene
ENSMUSG00000022483 | Col2a1
Description
collagen, type II, alpha 1 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:88452]
Coordinates
chr15:97829706-97835126:-
Coord C1 exon
chr15:97834840-97835126
Coord A exon
chr15:97830834-97831037
Coord C2 exon
chr15:97829706-97829722
Length
204 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
3' ss Seq
TCCCACCCCACTTGGTGCAGAGG
3' ss Score
4.25
5' ss Seq
GTGGTCGTA
5' ss Score
-11.41
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
GCCTTTGGAGCGACCGGGAGCATATAACTGGAGCCTCTGCCGGGGGAAGACGCAGAGCGCCGCTGGGCTGCCGGGTCTCCTGCCTCCTCCTGCTCCTAGGGCCTCCTGCATGAGGGAGCGGTAGAGACCCGGACCCGCTCCGTGCTCTGCCGCCTCGCTGCGCTTCGCCCGGGCCAGGCTCTGCCAGGCCTCGCGGTGAGCCATGATCCGCCTCGGGGCTCCCCAGTCGCTGGTGCTGCTGACGCTGCTCATCGCCGCGGTCCTACGGTGTCAGGGCCAGGATGCCC
Seq A exon
AGGAGGCTGGCAGCTGTCTGCAGAATGGGCAGAGGTATAAAGATAAGGATGTATGGAAGCCCTCATCTTGCCGCATCTGTGTGTGTGACACTGGGAATGTCCTCTGCGATGACATTATCTGTGAAGACCCAGACTGCCTCAACCCCGAGATCCCCTTCGGAGAGTGCTGTCCCATCTGCCCAGCTGACCTCGCCACTGCCAGTG
Seq C2 exon
GAAAATTAGGGCCAAAG
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSMUSG00000022483_CASSETTE1
Average complexity
S*
Mappability confidence:
100%=100=100%
Protein Impact
Alternative protein isoforms (Ref)
Show structural model
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.031 A=0.025 C2=0.767
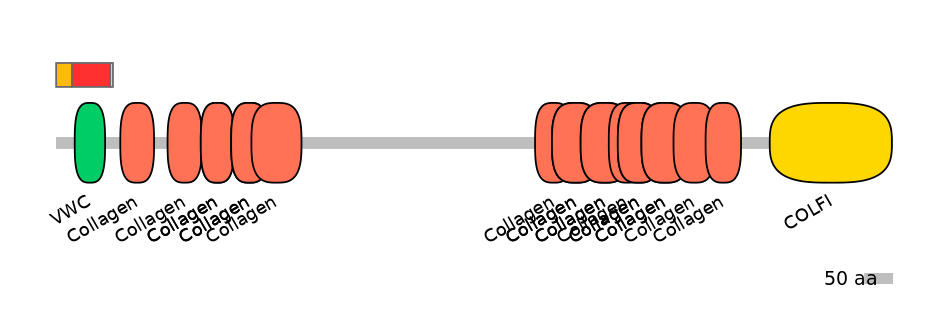
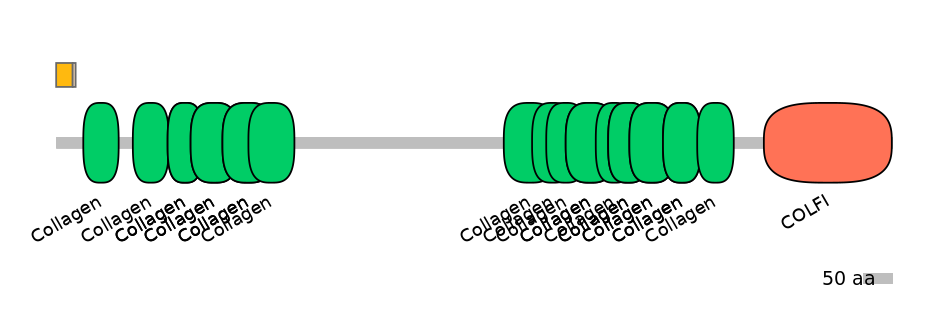
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF148281=Amnionless=PU(3.9=10.3)
A:
PF148281=Amnionless=FE(90.7=100),PF0009313=VWC=WD(100=79.7),PF0139113=Collagen=PU(3.4=2.9)
C2:
PF148281=Amnionless=PD(2.7=33.3),PF0139113=Collagen=FE(11.4=100)
Other Inclusion Isoforms:
Other Skipping Isoforms:
NA
Associated events
Other assemblies
Conservation
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
No suggested primer sequences
R:
No suggested primer sequences
Band lengths:
Functional annotations
There are 7 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 20730911
In this study, the authors show that procollagen IIA (IIA) (contains exon 2 (HsaEX0016515)), an isoform of the cartilage extracellular matrix protein encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript of Col2a1, is expressed in the prechordal plate and the anterior definitive endoderm. In the absence of IIA activity, the null mutants displayed a partially penetrant phenotype of loss of head tissues, holoprosencephaly, and loss of mid_facial structures, which is associated with reduced sonic hedgehog (Shh) expression in the prechordal mesoderm. Genetic interaction studies reveal that IIA function in forebrain and face development does not involve bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1A (BMPR1A)_ or NODAL_mediated signaling activity.
PMID: 22248926
The present study describes the generation of a knock-in mouse model to address the role of type II procollagen (Col2a1) alternative splicing in skeletal development and maintenance. Alternative splicing of Col2a1 precursor mRNA is a developmentally-regulated event that only occurs in chondrogenic tissue. Normally, chondroprogenitor cells synthesize predominantly exon 2-containing mRNA isoforms (type IIA and IID) while Col2a1 mRNA devoid of exon 2 (type IIB) is the major isoform produced by differentiated chondrocytes (Exon 2 id: HsaEX0016515). The biological significance of this IIA/IID to IIB splicing switch is not known. Utilizing a splice site targeting knock-in approach, a 4 nucleotide mutation was created to convert the 5' splice site of Col2a1 exon 2 from a weak, non-consensus sequence to a strong, consensus splice site. This resulted in apparent expression of only the IIA mRNA isoform, as confirmed in vitro by splicing of a type II procollagen mini-gene containing the 5' splice site mutation. To test the splice site targeting approach in vivo, homozygote mice engineered to retain IIA exon 2 (Col2a1(+ex2)) were generated. Chondrocytes from hindlimb epiphyseal cartilage of homozygote mice were shown to express only IIA mRNA and protein at all pre- and post-natal developmental stages analyzed (E12.5, E16.5, P0, P3, P7, P14, P28 and P70). As expected, type IIB procollagen was the major isoform produced in wild type cartilage at all post-natal time points. Col2a1(+ex2) homozygote mice are viable, appear healthy and display no overt phenotype to date. Negative results.
PMID: 10085302
Before chondrogenesis, type IIA procollagen (contains exon 2 (HsaEX0016515)) was synthesized by chondroprogenitor cells and deposited in the extracellular matrix. Immunoelectron microscopy revealed type IIA procollagen fibrils labeled with antibodies to NH2-propeptide (the amino acid stretch encoded by exon 2) at approximately 70 nm interval suggesting that the NH2-propeptide remains attached to the collagen molecule in the extracellular matrix. As differentiation proceeds, the cells switch synthesis from type IIA to IIB procollagen, and the newly synthesized type IIB collagen displaces the type IIA procollagen into the interterritorial matrix. To initiate studies on the function of type IIA procollagen, binding was tested between recombinant NH2-propeptide and various growth factors known to be involved in chondrogenesis. A solid phase binding assay showed no reaction with bFGF or IGF-1, however, binding was observed with TGF-beta1 and BMP-2, both known to induce endochondral bone formation. BMP-2, but not IGF-1, coimmunoprecipitated with type IIA NH2-propeptide. Recombinant type IIA NH2-propeptide and type IIA procollagen from media coimmunoprecipitated with BMP-2 while recombinant type IIB NH2-propeptide and all other forms of type II procollagens and mature collagen did not react with BMP-2
PMID: 10648240
A number of genetic and molecular studies have implicated Chordin in the regulation of dorsoventral patterning during gastrulation. Chordin, a BMP antagonist of 120 kDa, contains four small (about 70 amino acids each) cysteine-rich domains (CRs) of unknown function. In this study, the authors show that the Chordin CRs define a novel protein module for the binding and regulation of BMPs. The biological activity of Chordin resides in the CRs, especially in CR1 and CR3, which have dorsalizing activity in Xenopus embryo assays and bind BMP4 with dissociation constants in the nanomolar range. The activity of individual CRs, however, is 5- to 10-fold lower than that of full-length Chordin. These results shed light on the molecular mechanism by which Chordin/BMP complexes are regulated by the metalloprotease Xolloid, which cleaves in the vicinity of CR1 and CR3 and would release CR/BMP complexes with lower anti-BMP activity than intact Chordin. CR domains are found in other extracellular proteins such as procollagens. Full-length Xenopus procollagen IIA (contains the equivalent to exon 2 (HsaEX0016515) mRNA has dorsalizing activity in embryo microinjection assays and the CR domain is required for this activity as procollagen IIB (without exon 2 (HsaEX0016515)) does not have this effect. Similarly, a C. elegans cDNA containing five CR domains induces secondary axes in injected Xenopus embryos. These results suggest that CR modules may function in a number of extracellular proteins to regulate growth factor signalling. OF NOTE, THE POTENTIAL IMPACT OF EXON 2 ON TGF-BETA SIGNALING IS CONTROVERSIAL IN MAMMALS (reviewed in: 10.3109/03008207.2014.908860).
PMID: 11705992
In many embryonic tissues, type IIA (contains exon 2 (HsaEX0016515) procollagen is synthesized and deposited into the extracellular matrix containing the NH2-propeptide, the cysteine-rich domain of which binds to bone morphogenic proteins. To investigate whether matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) synthesized during development and disease can cleave the NH2 terminus of type II procollagens, the authors tested eight types of enzymes. Recombinant trimeric type IIA collagen NH2-propeptide encoded by exons 1?8 fused to the lectin domain of rat surfactant protein D was used as a substrate. The latter allowed trimerization of the propeptide domain and permitted isolation by saccharide affinity chromatography. Although MMPs 1, 2, and 8 did not show cleavage, MMPs 3, 7, 9, 13, and 14 cleaved the recombinant protein both at the telopeptide region and at the procollagen N-proteinase cleavage site. MMPs 7 and 13 demonstrated other cleavage sites in the type II collagen-specific region of the N-propeptide; MMP-7 had another cleavage site close to the COOH terminus of the cysteine-rich domain. To prove that an MMP can cleave the native type IIA procollagen in situ, the authors demonstrated that MMP-7 removes the NH2-propeptide from collagen fibrils in the extracellular matrix of fetal cartilage and identified the cleavage products.
PMID: 15466413
Chordin-like cysteine-rich (CR) repeats (also referred to as von Willebrand factor type C (VWC) modules) have been identified in approximately 200 extracellular matrix proteins. These repeats, named on the basis of amino acid conservation of 10 cysteine residues, have been shown to bind members of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily and are proposed to regulate growth factor signaling. Here the authors describe the intramolecular disulfide bonding, solution structure, and dynamics of a prototypical chordin-like CR repeat from procollagen IIA (CR(ColIIA)) (the CR repeat is encoded by exon 2 (HsaEX0016515)), which has been previously shown to bind TGF-beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2. The CR(ColIIA) structure manifests a two sub-domain architecture tethered by a flexible linkage. Initial structures were calculated using RosettaNMR, a de novo prediction method, and final structure calculations were performed using CANDID within CYANA. The N-terminal region contains mainly beta-sheet and the C-terminal region is more irregular with the fold constrained by disulfide bonds. Mobility between the N- and C-terminal sub-domains on a fast timescale was confirmed using NMR relaxation measurements. The authors speculate that the mobility between the two sub-domains may decrease upon ligand binding. Structure and sequence comparisons have revealed an evolutionary relationship between the N-terminal sub-domain of the CR module and the fibronectin type 1 domain, suggesting that these domains share a common ancestry. Based on the previously reported mapping of fibronectin binding sites for vascular endothelial growth factor to regions containing fibronectin type 1 domains, the authors discuss the possibility that this structural homology might also have functional relevance.
PMID: 16076844
[Regulation only]. Chondroprogenitor cells produce the type IIA procollagen isoform by splicing (including) exon 2 (HsaEX0016515) during pre-mRNA processing, whereas differentiated chondrocytes synthesize the type IIB procollagen isoform by exon 2 skipping (exclusion) (without HsaEX0016515). Using a COL2A1 mini-gene and chondrocytes at various stages of differentiation, the authors identified a non-classical consensus splicing sequence in intron 2 adjacent to the 5_ splice site, which is essential in regulating exon 2 splicing. RNA mapping confirmed this region contains secondary structure in the form of a stem-loop. Mutational analysis identified three cis elements within the conserved double-stranded stem region that are functional only in the context of the natural weak 5_ splice site of exon 2; they are 1) a uridine-rich enhancer element in all cell types tested except differentiated chondrocytes; 2) an adenine-rich silencer element, and 3) an enhancer cis element functional in the context of secondary structure.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- Pre-implantation embryo development
- Neural differentiation time course
- Muscular differentiation time course
- Spermatogenesis cell types
- Reprogramming of fibroblasts to iPSCs
- Hematopoietic precursors and cell types