RnoALTA0035233-1/2 @ rn6
Alternative 3'ss
Gene
ENSRNOG00000015049 | Scn5a
Description
sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 5 [Source:RGD Symbol;Acc:3637]
Coordinates
chr8:128201361-128203242:-
Coord C1 exon
chr8:128202802-128203242
Coord A exon
NA
Coord C2 exon
chr8:128201361-128201519
Length
0 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
5' ss Seq
CAGGTCAGC
5' ss Score
7.16
3' ss Seq
TCATGGGGTCTTTTCAGCAGGAA
3' ss Score
5.89
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
GTCCTGAATCTCTTCTTGGCCTTGCTGCTCAGCTCCTTCAGCGCAGACAACCTCACAGCCCCTGACGAGGATGGGGAGATGAACAACCTCCAGCTGGCCCTGGCTCGCATCCAGAGGGGCCTGCGCTTTGTCAAGCGGACCACCTGGGACTTCTGCTGCGGGATCCTGCGGCGGCGACCTAAGAAGCCCGCGGCTCTTGCCACCCACAGCCAGCTGCCCAGCTGTATCACCGCCCCCAGGTCCCCACCACCCCCAGAGGTGGAGAAGGTGCCCCCAGCCCGCAAGGAAACACGATTCGAGGAGGACAAGCGACCCGGCCAGGGCACCCCTGGGGATTCGGAGCCTGTGTGTGTGCCCATCGCCGTGGCTGAGTCAGACACTGAAGACCAGGAAGAGGATGAAGAGAACAGCCTTGGCACAGAGGAAGAGTCCAGCAAACAG
Seq A exon
NA
Seq C2 exon
GAATCCCAAGTTGTGTCTGGTGGCCACGAGCCCTACCAGGAGCCCAGGGCCTGGAGCCAGGTGTCAGAGACCACGTCCTCTGAAGCTGGGGCCAGTACATCTCAGGCAGACTGGCAGCAAGAGCAGAAAACGGAGCCCCAGGCCCCGGGGTGCGGTGAG
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSRNOG00000015049-25-27,25-26-1/2
Average complexity
Alt3
Mappability confidence:
NA
Protein Impact
Protein isoform when splice site is used (Ref)
No structure available
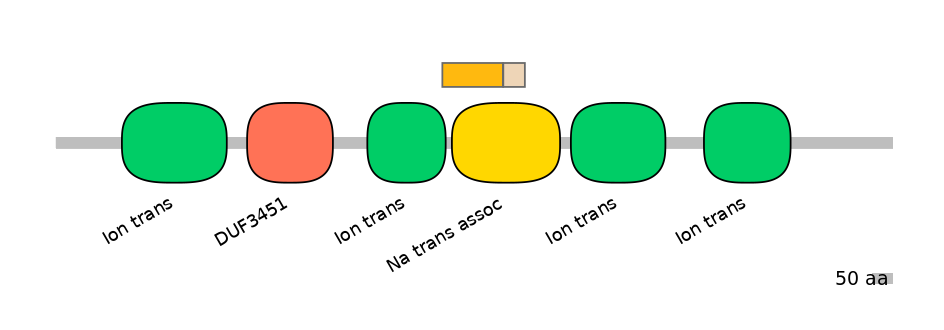
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.531 A=NA C2=1.000
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF0052026=Ion_trans=PD(4.2=5.4),PF065128=Na_trans_assoc=PU(46.9=83.7)
A:
NA
C2:
PF065128=Na_trans_assoc=FE(19.8=100)
Main Skipping Isoform:
NA
Other Skipping Isoforms:
NA
Associated events
Conservation
Chicken
(galGal4)
No conservation detected
Chicken
(galGal3)
No conservation detected
Zebrafish
(danRer10)
No conservation detected
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
TTGGCACAGAGGAAGAGTCCA
R:
TCTCTGACACCTGGCTCCAG
Band lengths:
99-102
Functional annotations
There are 7 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 14500339
The effect of common polymorphisms in the alpha unit of the cardiac sodium channel (SCN5A) was examined in the two splice variants that differ in the presence/absence a single amino acid; Q1077 (included when HsaALTA0007521-2/2 is used, excluded when HsaALTA0007521-1/2 is used). When transiently overexpressed in HEK-293 cells, the common SCN5A variants had a more positive mid-point of the voltage dependence of inactivation than the standard clone hH1. Also, channels containing Q1077 (HsaALTA0007521-2/2) expressed smaller currents. When H558R was present with Q1077 ([H558R]), current expression was profoundly reduced despite normal trafficking to the cell surface.
PMID: 15992732
Eight common (>0.5%) polymorphisms of SCN5A have been described in the US population. Every human also continuously generates two wild-type (WT) splice variants, one with a glutamine residue at position 1077 (Q1077) (included by using alternative splice site HsaALTA0007521-2/2) and one lacking this glutamine (Q1077del) (uses HsaALTA0007521-1/2). One polymorphism (H558R) has been studied in both splice variants, five polymorphisms (R34C, R481W, S524Y, P1090L,V1951L) have not been previously studied, and two polymorphisms (S1103Y and R1193Q) have been studied in only one of the two splice variants. This study examined the electrophysiologic molecular phenotype of the eight common polymorphisms in the two human splice variants of SCN5A. Currents from 16 channels (all polymorphisms in both splice variants) were determined by voltage clamp and compared with WT after expression in HEK-293 cells. Six of eight polymorphisms showed a distinct phenotype that depended upon the background splice variant used for expression. Only R34C and V1951L showed no functional differences. S524Y showed a dramatic reduction in current density in the Q1077 background similar to that previously described for H558R. Four other polymorphisms (R481W, P1090L, S1103Y, R1193Q) showed shifts in activation, inactivation, or recovery that depended upon the splice variants. Shifts of a similar magnitude have been reported for arrhythmia syndrome mutations and are thought to be pathogenic.
PMID: 16632547
Mutations in the cardiac Na+ channel gene SCN5A cause loss of function and underlie arrhythmia syndromes. SCN5A in humans has two splice variants, one lacking a glutamine at position 1077 (Q1077del) (uses HsaALTA0007521-1/2) and one containing Q1077 (uses HsaALTA0007521-2/2). The authors investigated the effect of splice variant background on loss of function and rescue for G1406R, a mutation reported to cause Brugada syndrome. Mutant and wild-type (WT) channels in both backgrounds were transfected into HEK-293 cells and incubated for up to 72 h with and without mexiletine. At 8 h, neither current nor cell surface expression was observed for the mutant in either background, but both were present in WT channels. At 24 h, small (
PMID: 21167004
Two novel rare variants of the cardiac sodium channel (SCN5A) rare variants, R222Q and I1835T, segregated with dilated cardiomyopathay (DCM) in two families with affected individuals homozygous or heterozygous for the common SCN5A polymorphism H558R. cDNAs with each rare variant were constructed in the common Q1077del (uses HsaALTA0007521-1/2) or Q1077 (uses HsaALTA0007521-2/2) splice variant backgrounds with and without the H558R polymorphism and expressed in HEK293 cells. Sodium current (I Na) was studied for each using whole_cell voltage clamp. In the Q1077del background I Na densities of R222Q and I1835T were not different from wild type, but the combined variants of R222Q/H558R, I1835T/H558R caused approximately 35% and approximately 30% reduction, respectively, and each showed slower recovery from inactivation. In the Q1077del background R222Q and R222Q/H558R also exhibited a significant negative shift in both activation and inactivation while I1835T/H558R showed a significant negative shift in inactivation that tended to decrease window current. In contrast, expression in the Q1077 background showed no changes in peak I Na densities, decay, or recovery from inactivation for R222Q/H558R and I1835T/H558R.
PMID: 21552533
Negative results. Nine Nav1.5 (SCN5A) splice variants are known. Four of them, namely Nav1.5a, Nav1.5c, Nav1.5d, and Nav1.5e, generate functional channels in heterologous expression systems. In the present study, the authors systematically investigated electrophysiological properties of mutant T1620K channels in the background of all known functional Nav1.5 splice variants in HEK293 cells. This mutation is associated with two cardiac excitation disorders: long QT syndrome type 3 (LQT3) and isolated cardiac conduction disease (CCD). When investigating the effect of the T1620K mutation, the authors noticed similar channel defects in the background of hNav1.5, hNav1.5a, and hNav1.5c. In contrast, the hNav1.5d background produced differential effects: In the mutant channel, some gain-of-function features did not emerge, whereas loss-of-function became more pronounced. In case of hNav1.5e, the neonatal variant of hNav1.5, both the splice variant itself as well as the corresponding mutant channel showed electrophysiological properties that were distinct from the wild-type and mutant reference channels, hNav1.5 and T1620K, respectively. In conclusion, these data show that alternative splicing is a mechanism capable of generating a variety of functionally distinct wild-type and mutant hNav1.5 channels. Thus, the cellular splicing machinery is a potential player affecting genotype-phenotype correlations in SCN5A channelopathies. (About variants: Variant a and c differs from the canonical variant by skipping exon 18 (HsaEX0056556), and including Q1077 (HsaALTA0007521-2/2), respectively. Negative results for those. Variant D seems to use alternative splice sites in exon 17 (not in VastDB), and variant E uses the neonatal version of the ME exon (HsaEX0056558), while the other variants use the adult version (HsaEX0056559)).
PMID: 25923670
The alpha-subunit of the cardiac sodium channel (SCN5A) is a susceptibility gene for type 3 long QT syndrome. Sodium current (INa) dysfunction from mutated SCN5A can depend upon the splice variant background in which it is expressed and also upon environmental factors such as acidosis. S1787N was reported previously as a LQT3-associated mutation and has also been observed in 1 of 295 healthy white controls. Here, the authors determined the in vitro phenotype of SCN5A-S1787N to assess its possible pathogenicity. The authors engineered S1787N into the two most common splice SCN5A isoforms; the major isoform lacking Q1077 (Q1077del) (uses HsaALTA0007521-1/2) and the minor isoform containing Q1077 (uses HsaALTA0007521-2/2), and expressed the constructs in HEK293 cells for electrophysiological study. Macroscopic voltage-gated INa were measured using whole-cell patch clamp techniques. The authors applied intracellular solutions with pH 7.4 or pH 6.7. S1787N in the Q1077 background had WT-like INa including peak INa density, activation and inactivation parameters, and late INa amplitude in both pH 7.4 and pH 6.7. However, with S1787N in the Q1077del background, the percentages of INa late/peak were increased by 2.1 fold in pH 7.4 and by 2.9 fold in pH 6.7 when compared to WT.
PMID: 26382759
This study examines the effect of co-expression of either of the cardiac sodium channel (SCN5A) major splice variants (differs in presence/absece of Q1077; absence comes from use of HsaALTA0007521-1/2, while presence comes from use of HsaALTA0007521-2/2) with the Fyn tyrosine kinase on channel activity. Whole-cell ionic currents were recorded in patch clamp experiments to examine the modulation of Nav1.5 channel variants by Fyn kinase, which indicated a hyperpolarizing shift of 9.68 mV in fast inactivation of Q-del. In contrast, a depolarizing shift of 8.77 mV in fast inactivation was observed in the case of Q-pre, while activation curves remained unaltered for both splice variants. This differential modulation in fast inactivation was further assessed by mutating tyrosine 1495 to phenylalanine in the inactivation loop, which completely removed the modulatory effect of Fyn kinase in Q-pre splice variant, while in Q-del variant hyperpolarizing shift in fast inactivation was reduced to 4.74 mV. Finally, the modulatory effect of Fyn kinase was compensated at a mid-value of 94.63 ? 0.34, when both splice variants were co-expressed at a normal physiological ratio.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]