MmuALTD0011277-1/2 @ mm9
Alternative 5'ss
Gene
ENSMUSG00000034573 | Ptpn13
Description
protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 13 [Source:MGI Symbol;Acc:MGI:103293]
Coordinates
chr5:103985107-103986991:+
Coord C1 exon
chr5:103985107-103985238
Coord A exon
NA
Coord C2 exon
chr5:103986898-103986991
Length
0 bp
Sequences
Splice sites
5' ss Seq
ACGGTACTG
5' ss Score
5.88
3' ss Seq
ACTTTGTTTTGTCTATTTAGGGA
3' ss Score
10.65
Exon sequences
Seq C1 exon
GAACCTTCCTCCTCACTGAGTACATCGAACAAAACGAGCTTTCCAACCTCGTCTGCGTCACCTCCTAAGCCCGGAGACACGTTTGAGGTTGAGCTGGCTAAAACTGATGGCAGCCTGGGGATAAGTGTCACG
Seq A exon
NA
Seq C2 exon
GGAGGTGTGAATACCAGCGTCCGACATGGTGGTATTTATGTGAAAGCCATTATTCCCAAAGGAGCGGCAGAGTCAGATGGCAGAATTCACAAAG
VastDB Features
Vast-tools module Information
Secondary ID
ENSMUSG00000034573-31-33,32-33-1/2
Average complexity
Alt5
Mappability confidence:
NA
Protein Impact
Protein isoform when splice site is used (Ref)
No structure available
Features
Disorder rate (Iupred):
C1=0.955 A=NA C2=0.594
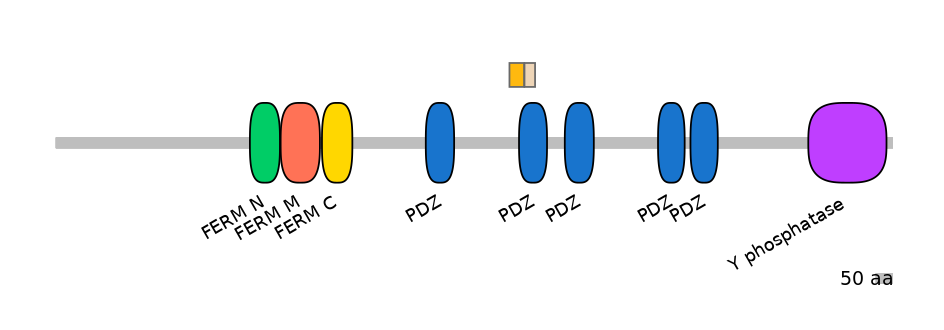
Domain overlap (PFAM):
C1:
PF0059519=PDZ=PU(18.1=34.1)
A:
NA
C2:
PF0059519=PDZ=FE(37.3=100)
Main Skipping Isoform:
NA
Other Skipping Isoforms:
NA
Associated events
Conservation
Fruitfly
(dm6)
No conservation detected
Primers PCR
Suggestions for RT-PCR validation
F:
CTAAGCCCGGAGACACGTTTG
R:
AAATACCACCATGTCGGACGC
Band lengths:
105-120
Functional annotations
There are 8 annotated functions for this event
PMID: 10951583
Here the authors describe a novel interaction between the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) protein and the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-BL carrying five PDZ protein?protein interaction domains. Exclusively, the second PDZ domain (PDZ2) of PTP-BL is binding to the extreme C-terminus of the APC protein, as determined by yeast two-hybrid studies. Using surface plasmon resonance analysis the authors established a dissociation constant (KD) of 8.1_10_9_M. The authors find that a naturally occurring splice insertion of five amino acids (PDZ2b) (uses HsaALTD0005161-2/2) abolishes its binding affinity to the APC protein (comparedd to the PDZ2a variant, that uses HsaALTD0005161-1/2).
PMID: 14596806
Two versions of the PDZ2 domain of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-Bas/human PTP-BL are generated by alternative splicing. The domains differ by the insertion of five amino acid residues (via use of HsaALTD0005161-2/2) and their affinity to the tumour suppressor protein APC. Whereas PDZ2a (uses HsaALTD0005161-1/2) is able to bind APC in the nanomolar range, PDZ2b (uses HsaALTD0005161-2/2) shows no apparent interaction with APC. Here the solution structure of the splicing variant of PDZ2 with the insertion has been determined using 2D and 3D heteronuclear NMR experiments. The structural reason for the changed binding specificity is the reorientation of the loop with extra five amino acid residues, which folds back onto beta-strands two and three. In addition the side-chain of Lys32 closes the binding site of the APC binding protein and the two helices, especially alpha-helix 2, change their relative position to the protein core. Consecutively, the binding site is sterically no longer fully accessible. From the NMR-titration studies with a C-terminal APC-peptide the affinity of the peptide with the protein can be estimated as 540(+/-40)microM. The binding site encompasses part of the analogous binding site of PDZ2a as already described previously, yet specific interaction sites are abolished by the insertion of amino acids in PDZ2b. As shown by high-affinity chromatography, GST-PDZ2b and GST-PDZ2a bind to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) micelles with a dissociation constant K(D) of 21 microM and 55 microM, respectively. In line with these data PDZ2b binds isolated, dissolved PIP(2) and PIP(3) (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate) molecules specifically with a lower K(D) of 230(+/-20)microM as detected by NMR spectroscopy. The binding site could be located by these studies and involves the residues Ile24, Val26, Val70, Asn71, Gly77, Ala78, Glu85, Arg88, Gly91 and Gln92. PIP(2) and PIP(3) binding takes place in the groove of the PDZ domain that is normally part of the APC binding site.
PMID: 14725761
PTP-BL is a large phosphatase that is implicated in cellular processes as diverse as cytokinesis, actin-cytoskeletal rearrangement, and apoptosis. Five PDZ domains mediate its cellular role by binding to the C termini of target proteins, forming multiprotein complexes. The second PDZ domain (PDZ2) (splice variant using HsaALTD0005161-1/2) binds to the C termini of the tumor suppressor protein APC and the LIM domain-containing protein RIL; however, in one splice variant, PDZ2as, a 5 residue insertion (via use of HsaALTD0005161-2/2) abrogates this binding. The insert causes distinct structural and dynamical changes in the alternatively spliced PDZ2: enlarging the L1 loop between beta2 and beta3, both lengthening and changing the orientation of the alpha2 helix, giving the base of the binding pocket less flexibility to accommodate ligands, and destabilizing the entire domain. These changes render the binding pocket incapable of binding C termini, possibly having implications in the functional role of PTP-BL.
PMID: 25788329
PDZ domains are the most prominent biological structural domains involved in protein-protein interactions in the human cell. The second PDZ domain of the protein tyrosine phosphatase BL (PDZ2) interacts and binds the C-termini of the tumour suppressor protein APC and of the LIM domain-containing protein RIL. One isoform of protein tyrosine phosphatase BL's PDZ2 domain (PDZ2as) involves an alternative spliced form that exhibits an insertion of 5 residues in a loop (happens via use of HsaALTD0005161-2/2 instead of HsaALTD0005161-1/2). PDZ2as abrogates binding to its partners, even if the insertion is directly located in its binding pocket. Here, the authors investigate the folding and function of PDZ2as, in comparison to the previously characterized PDZ2 domain. Data reveal that, whilst the thermodynamic stability of PDZ2as appears as nearly identical to that of PDZ2, the insertion of 5 amino acids induces formation of some weak transient non-native interactions in the folding transition state, as mirrored by a concomitant increase of both the folding and unfolding rate constants. From a functional perspective, the authors show that the decrease in affinity is caused by a pronounced decrease of the association rate constants (by nearly ten fold), with no effect on the microscopic dissociation rate constants.
PMID: 10951583
Here the authors describe a novel interaction between the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) protein and the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-BL carrying five PDZ protein?protein interaction domains. Exclusively, the second PDZ domain (PDZ2) of PTP-BL is binding to the extreme C-terminus of the APC protein, as determined by yeast two-hybrid studies. Using surface plasmon resonance analysis the authors established a dissociation constant (KD) of 8.1_10_9_M. The authors find that a naturally occurring splice insertion of five amino acids (PDZ2b) (uses HsaALTD0005161-2/2) abolishes its binding affinity to the APC protein (comparedd to the PDZ2a variant, that uses HsaALTD0005161-1/2).
PMID: 14596806
Two versions of the PDZ2 domain of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-Bas/human PTP-BL are generated by alternative splicing. The domains differ by the insertion of five amino acid residues (via use of HsaALTD0005161-2/2) and their affinity to the tumour suppressor protein APC. Whereas PDZ2a (uses HsaALTD0005161-1/2) is able to bind APC in the nanomolar range, PDZ2b (uses HsaALTD0005161-2/2) shows no apparent interaction with APC. Here the solution structure of the splicing variant of PDZ2 with the insertion has been determined using 2D and 3D heteronuclear NMR experiments. The structural reason for the changed binding specificity is the reorientation of the loop with extra five amino acid residues, which folds back onto beta-strands two and three. In addition the side-chain of Lys32 closes the binding site of the APC binding protein and the two helices, especially alpha-helix 2, change their relative position to the protein core. Consecutively, the binding site is sterically no longer fully accessible. From the NMR-titration studies with a C-terminal APC-peptide the affinity of the peptide with the protein can be estimated as 540(+/-40)microM. The binding site encompasses part of the analogous binding site of PDZ2a as already described previously, yet specific interaction sites are abolished by the insertion of amino acids in PDZ2b. As shown by high-affinity chromatography, GST-PDZ2b and GST-PDZ2a bind to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) micelles with a dissociation constant K(D) of 21 microM and 55 microM, respectively. In line with these data PDZ2b binds isolated, dissolved PIP(2) and PIP(3) (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate) molecules specifically with a lower K(D) of 230(+/-20)microM as detected by NMR spectroscopy. The binding site could be located by these studies and involves the residues Ile24, Val26, Val70, Asn71, Gly77, Ala78, Glu85, Arg88, Gly91 and Gln92. PIP(2) and PIP(3) binding takes place in the groove of the PDZ domain that is normally part of the APC binding site.
PMID: 14725761
PTP-BL is a large phosphatase that is implicated in cellular processes as diverse as cytokinesis, actin-cytoskeletal rearrangement, and apoptosis. Five PDZ domains mediate its cellular role by binding to the C termini of target proteins, forming multiprotein complexes. The second PDZ domain (PDZ2) (splice variant using HsaALTD0005161-1/2) binds to the C termini of the tumor suppressor protein APC and the LIM domain-containing protein RIL; however, in one splice variant, PDZ2as, a 5 residue insertion (via use of HsaALTD0005161-2/2) abrogates this binding. The insert causes distinct structural and dynamical changes in the alternatively spliced PDZ2: enlarging the L1 loop between beta2 and beta3, both lengthening and changing the orientation of the alpha2 helix, giving the base of the binding pocket less flexibility to accommodate ligands, and destabilizing the entire domain. These changes render the binding pocket incapable of binding C termini, possibly having implications in the functional role of PTP-BL.
PMID: 25788329
PDZ domains are the most prominent biological structural domains involved in protein-protein interactions in the human cell. The second PDZ domain of the protein tyrosine phosphatase BL (PDZ2) interacts and binds the C-termini of the tumour suppressor protein APC and of the LIM domain-containing protein RIL. One isoform of protein tyrosine phosphatase BL's PDZ2 domain (PDZ2as) involves an alternative spliced form that exhibits an insertion of 5 residues in a loop (happens via use of HsaALTD0005161-2/2 instead of HsaALTD0005161-1/2). PDZ2as abrogates binding to its partners, even if the insertion is directly located in its binding pocket. Here, the authors investigate the folding and function of PDZ2as, in comparison to the previously characterized PDZ2 domain. Data reveal that, whilst the thermodynamic stability of PDZ2as appears as nearly identical to that of PDZ2, the insertion of 5 amino acids induces formation of some weak transient non-native interactions in the folding transition state, as mirrored by a concomitant increase of both the folding and unfolding rate constants. From a functional perspective, the authors show that the decrease in affinity is caused by a pronounced decrease of the association rate constants (by nearly ten fold), with no effect on the microscopic dissociation rate constants.
GENOMIC CONTEXT[edit]
INCLUSION PATTERN[edit]
SPECIAL DATASETS
- Pre-implantation embryo development
- Neural differentiation time course
- Muscular differentiation time course
- Spermatogenesis cell types
- Reprogramming of fibroblasts to iPSCs
- Hematopoietic precursors and cell types
Other AS DBs: